The Physiotherapy has many concepts that sometimes, when we go to the specialist, we do not understand. On this space, we are going to learn a little of some words that physiotherapists use daily with a patient:
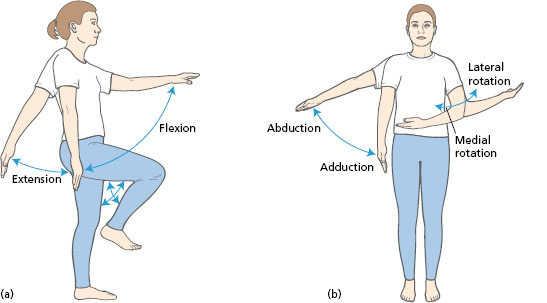
-Abduction - A movement of a limb away from midline or the center of the body.
-Adduction - A movement of a limb toward midline or the center of the body.
-Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) - refer to daily self-care activities like bathing, dressing, toileting, feeding and meal preparation.
- Ataxia - Muscular incoordination especially manifested when voluntary muscular movements are attempted.
- Bilateral - Pertaining to two sides of the body, as in: both arms or both legs.
- Bilateral - Pertaining to two sides of the body, as in: both arms or both legs.
-Cartilage- It is connective tissue that covers the ends of bones and acts as a cushion to absorb shock and a smooth surface to decrease friction between two or more bones in a moving joint.
- Contracture - occurs when a joint loses motion due to structural changes in the muscle, ligaments or tendons. Contractures are common in stroke as a result of lack of movement.
- Core - Pertaining to the trunk (primarily abdominals and back).
- Deformity - A major difference in the shape of a body part compared to what is normal for that body part. Deformity is most often seen in arthritis and sometimes in severe burn cases.
- Dissociation - To separate. For example: one extremity/limb performs a movement without the other extremity doing the same or similar movement at the same time.
- Distal - Farthest from the center, from midline or from the trunk.
- Extension - A straightening or backward movement of the spine or limbs.
- External rotation - An outward turning of the limb away from the body.
- Fine motor - the action involving the small muscles of the hands, as in handwriting, sewing or knitting.
- Flexion - A bending or forward movement of the spine or limbs.
- Gross Motor - Refers to movement of large muscle groups.Gross motor involves the larger muscle groups of the body to perform bigger movements such as walking or kicking a ball.
- Hamstrings - A muscle group on the back of the thigh that can bend/flex the knee and straighten/extend the hip.
- Hyperextension - Excessive movement in the direction of extension.
- Hypermobility - Movement beyond normal range of motion.
- Hypertonic - Muscle tone higher than normal; resistance to passive movement; in extreme form = spasticity.
- Hypotonic - Less than normal tone; floppy.
- Internal rotation - An inward turning of the limb toward the body.
- Instability - Lack of firmness in weight-bearing. Difficulty maintaining weight bearing.
- Kyphosis - An increased convexity in the curvature of the thoracic spine (hunchback).
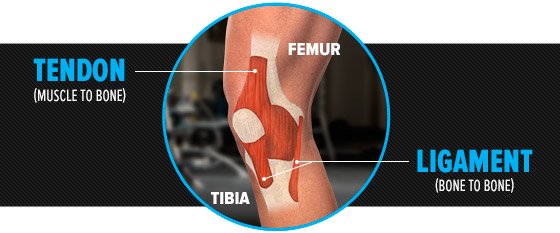
- Ligaments- they are the soft tissues that hold two or more bones together.
- Lordosis - An anterior/forward curvature of the lumbar and cervical vertebrae (spine). An increase is often referred to as “sway-back”.
- Lumbar - Pertaining to the low back.
- Motor Control - The ability of the Central Nervous System to regulate or direct the musculoskeletal system in a purposeful act.
- Motor Planning - The ability to organize and perform movement in a meaningful manner.
- Prone - Lying on the belly, face down.
- Proprioception - The awareness of posture, movement, changes in equilibrium, and the knowledge of position, weight, and resistance of objects in relation to the body. Sensed by muscles, tendons, and soft tissue.
- Proximal - Nearest to the point of attachment or center of the body.
- Quadriceps - A large muscle group on the anterior/front surface of the thigh responsible for knee extension.
- Range of Motion - A measure of the amount of movement/motion available at any given joint of the body.
- Reflex - An involuntary/automatic response to a stimulus.
- Sacral - The triangular-shaped bone below the lumbar spine formed, typically, by the fusion of 5 vertebrae.
- Spasticity - Hypertension of muscles causing stiff and awkward movements.
- Supine - Lying on the back, face up.
-Tactile Defensiveness - A negative response or increased sensitivity to touch.
- Tendon- It is the non-contractile unit that transmits the force of the muscle to the bone. Tendons connect muscles to bones.
- Thoracic - Pertaining to or affecting the chest or upper back.
- Tone (muscle) - The degree of tension normally present in the resting state of a muscle.
Curiosities-on:
No comments:
Post a Comment